Insights
The Power of Self-Service Analytics: Data for Everyone

Data is all around us, but what can we do with it? How can we use data to make better decisions, improve our processes, and make our customers more satisfied? That’s where data analytics comes in: transforming raw data into valuable insights.
However, analytics is not reserved for experts or specialists alone. Analytics is for everyone who works with data or is influenced by it. This means that every employee in an organization should have the ability to understand, analyze, and use data. This is the concept of data democratization: making data and information accessible to everyone who needs it.
One way to promote data democratization is by offering self-service analytics. Self-service analytics is a form of analytics where the user can choose the tools and information they need without depending on a central department or an external party. It empowers users to ask their own questions, find answers, and take action based on data and information.
Why is Self-Service Analytics Important?
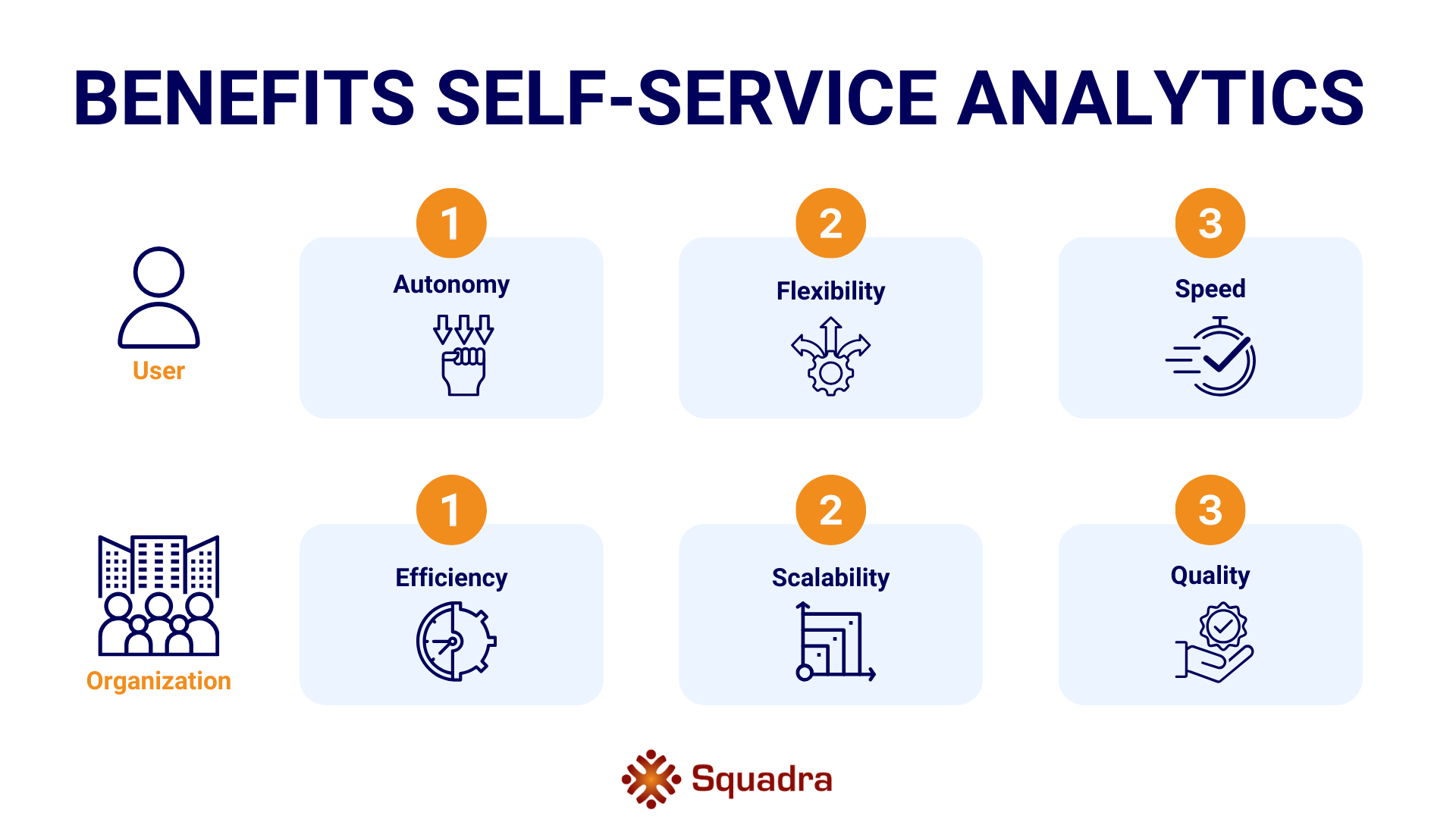
For the User: Autonomy, Flexibility and Speed
Self-service analytics has several benefits for both the user and the organization. For the user, it means more autonomy, flexibility, and speed. Users can determine which data and information are relevant to their work, how that data is presented, and which analyses are applied. They don’t have to wait for a report or dashboard from another department but can directly work with the data. This leads to increased engagement, trust, and innovation.
For the Organization: Efficiency, Scalability and Quality
For the organization, self-service analytics means increased efficiency, scalability, and quality. The organization spends less time and resources delivering standard reports or dashboards that may not align with users’ specific needs. Instead, the focus can shift to collecting, cleaning, and securing data, standardizing information, and providing a platform for users to conduct their own analyses. This results in more consistency, transparency, and data reliability.
How Does Self-Service Analytics Work?
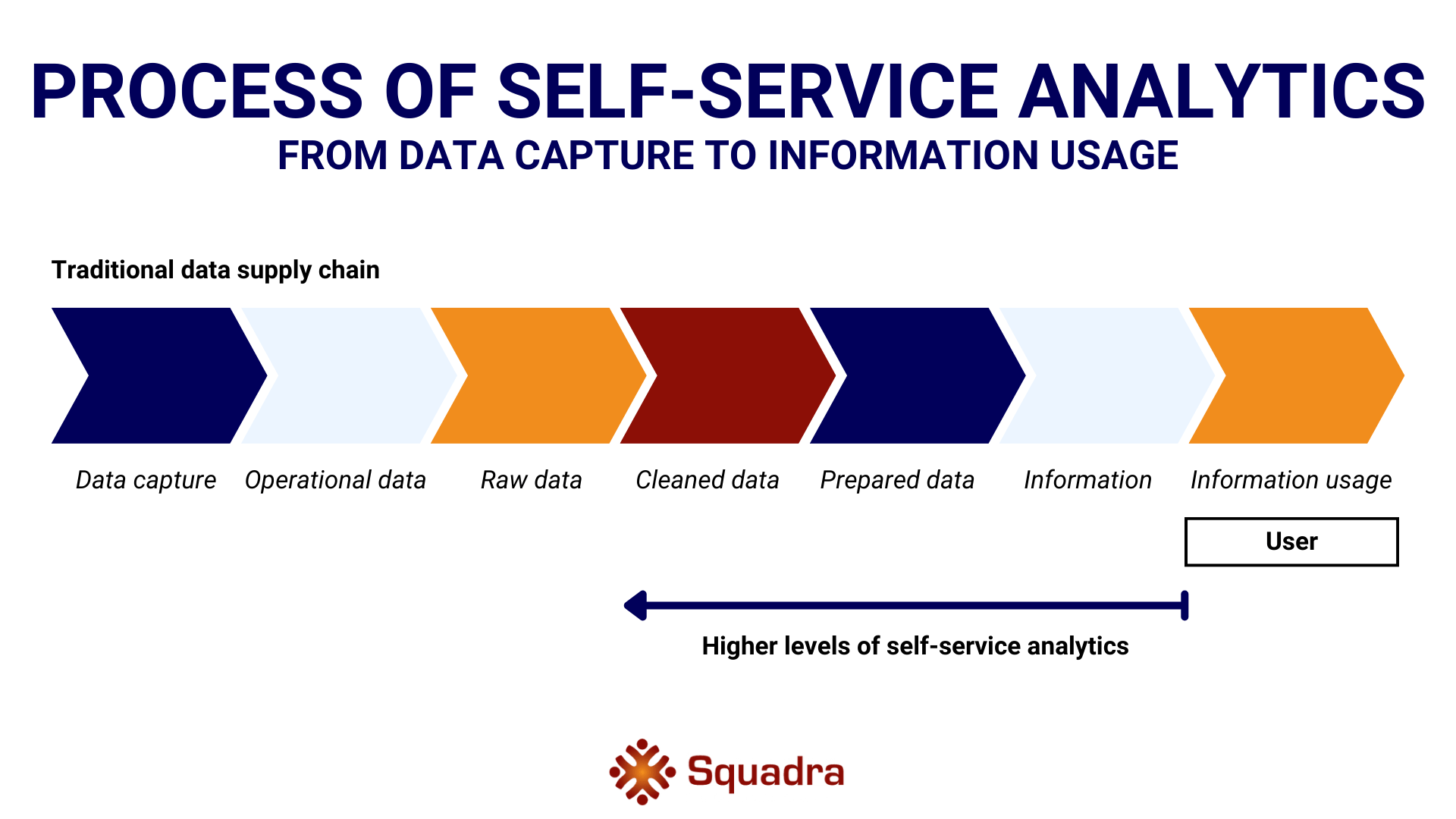
To understand how self-service analytics works, we need to look at the data transformation process. Data transformation is the process of converting raw data into a usable form. It involves various steps such as collecting (e.g., customer feedback through online surveys), storing (in databases or clouds), cleaning (removing duplicate or inaccurate data), preparing (organizing and structuring data), analyzing (using statistical tools), and visualizing (through charts or dashboards) data.
The image below illustrates how the data transformation process looks in a traditional and a self-service data supply chain. A data supply chain is the sequence of activities required to transform data into valuable insights for users. To distinguish between raw data and insights, the term “information” is often used for the latter.
In the traditional process, users rely on a central department or an external party to provide the data and tools they need. They have little or no control over the data and must wait for a report or dashboard that may not suit their specific needs. This can be compared to waiting for monthly financial reports provided by the finance department. This process is slow, rigid, and inefficient.
In contrast, the self-service process allows users to choose the data and tools they need independently. They have more control over data processing and can find answers and take action on their own. For example, marketing staff can have direct access to customer feedback and analyze the data to adjust marketing strategies immediately. This process is fast, flexible, and efficient.
The self-service process is made possible by a reliable and secure data environment where data is structured, cleaned, and prepared for analysis. Users have access to a self-service analytics platform, where they can use various tools to analyze and visualize data. The self-service analytics platform also provides support and guidance to users to improve their data literacy.
How to Implement Self-Service Analysitcs in Your Organization?
But how do you implement self-service analytics in your organization? That depends on your target audience and objectives.
1. Segment Your Target Audience
Not every user has the same need for or skill with analytics. Some users just want an overview of key indicators or trends, while others want to delve deeper into details or perform more complex analyses. Some users are satisfied with a dashboard or chart, while others prefer working with raw data or creating their own visualizations.
Therefore, it’s crucial to segment your target audience and understand their needs. A possible segmentation of your target audience includes:
- Data Specialists: Users with high analytical skills who primarily need unstructured data. They want to conduct innovative and experimental analyses, creating new knowledge or value. They benefit from self-service tools that allow them to explore, discover, test, and optimize data on their own.
- Business Users: Users with average analytical skills who primarily need structured information. They want quick and easy insights into data to support their daily tasks or decisions. They benefit from self-service tools that enable them to select, filter, sort, and visualize information on their own. They mainly use existing data and do not add or modify new data.
- Consumers: Users with low analytical needs who primarily need predefined information. They only want to see the key results or recommendations and have no interaction with the data. They benefit from self-service tools that allow them to consume, share, or review information on their own. They don’t use data but only receive it.
2. Define Your Objectives
After segmenting your target audience, you need to define your objectives. What do you want to achieve with self-service analytics? What benefits do you expect for your users and your organization? How will you measure your success? Some possible objectives include:
- Improving the Data Culture: Want users to become more data-driven, see data as a strategic resource for their work, have more confidence in data, and derive more value from it. Success can be measured by monitoring the number of data analyses, data sources, data users, or data feedbacks.
- Increasing Productivity: Want users to do their work faster and better, wasting less time and effort searching, processing, or interpreting data. Want them to focus more on their core tasks and be less dependent on others for their data needs. Success can be measured by monitoring throughput, quality, efficiency, or user satisfaction.
- Promoting Innovation: Want users to become more creative and experimental, discovering new possibilities or solutions with data. Want them to take more risks and make mistakes, learning from their data experiences. Want them to have more impact on their environment and create more value for customers or stakeholders. Success can be measured by monitoring the number of new ideas, projects, insights, or customers.
Best Practices for Using and Implementing Self-Service Analytics
Finally, you can make optimal use of self-service analytics and implement it successfully by following some best practices and avoiding pitfalls. Here are some tips or recommendations that can help you make your self-service analytics successful:

1. Don’t Underestimate the Groundwork
One of the biggest misconceptions about self-service analytics is the illusion that it requires less preparatory work. On the contrary, to obtain valuable insights, a solid foundation of structured data, clear definitions, and accessible tools must be established. It is essential to understand that autonomy does not mean users can operate without guidance but rather that the preparation of data and systems plays a crucial role.
2. Aim for Standardization
While self-service analytics allows for flexibility, it requires some degree of standardization. Define common standards for data, access methods, and tools used. This standardization not only facilitates collaboration but also ensures that users have a uniform foundation to work from.
3. Invest in Training and Guidance
The key to successful self-service analytics lies in good training and guidance. Ensure that users understand not only the tools but also how to interpret and analyze data and information. Promoting data literacy is an ongoing effort that enables users to confidently and effectively handle data.
4. Embrace Cultural Change
Cultural change is inevitable when implementing self-service analytics. It is not sufficient to merely introduce the tools; it is about creating a culture where people are intrinsically motivated to work with data. Utilize ambassadors actively involved in the process, acting as catalysts for change. Inspire and motivate instead of forcing change.
5. Keep it Interactive and Fast
One of the biggest obstacles to user adoption is slowness. Make self-service analytics interactive and fast. Users should navigate data effortlessly, find answers immediately, and be capable of quick action. A slow and complicated experience will lead to frustration and ultimately user disengagement.
These essential elements highlight the reality of self-service analytics and provide a solid foundation for successful implementation. It is not just about tools but creating an environment where users are genuinely empowered by data.
Conclusion
Self-service analytics is a powerful way to achieve data democratization, allowing every user to understand, analyze, and use data without relying on others. It brings benefits to both the user and the organization, such as increased autonomy, flexibility, speed, efficiency, scalability, and quality.
However, self-service analytics is not something you can implement casually. It requires careful preparation, standardization, training, guidance, and cultural change. By following best practices and avoiding pitfalls, you can create a successful self-service analytics environment where everyone is empowered by data.

